Eron JJ. Lancet Infect Dis. 2011 Dec;11(12):907-15
Head-to-head comparative trials for first line ART since 2006
» INSTI vs INSTI
» RAL QD + FTC/TDF vs RAL BID + FTC/TDF
RAL, FTC/TDF, TDF, FTC
- At 48 weeks of treatment, RAL QD was not non-inferior to RAL BID, in combination with TDF/FTC
- Virologic failure was more common with once-daily dosing especially in patients with baseline HIV RNA > 100 000 c/mL
- More patients in the once-daily group than in the twice-daily group had resistance emergence to both RAL and FTC at the time of virological failure
- Patients in the once-daily group with low pharmacokinetic values and high baseline viral loads were at particular risk of treatment failure
- Despite a high response rate, RAL at 800 mg QD cannot be recommended in place of twice-daily dosing for first-line antiretroviral therapy
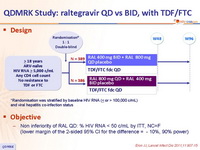
Design :

*Randomisation was stratified by baseline HIV RNA (< or > 100,000 c/mL) and viral hepatitis co-infection status
Objective :
- Non inferiority of RAL QD: % HIV RNA < 50 c/mL by ITT, NC=F (lower margin of the 2-sided 95% CI for the difference = - 10%, 90% power)
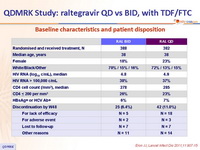
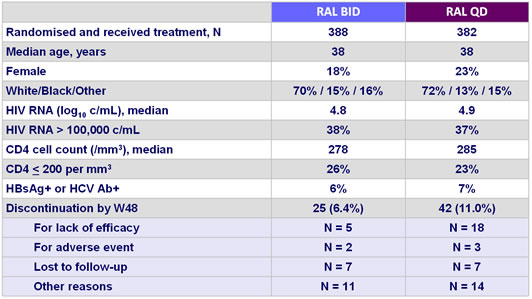
Baseline characteristics and patient disposition :
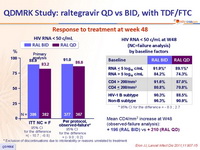
Response to treatment at week 48 :
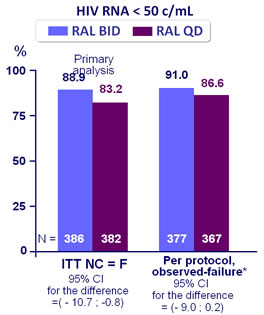
* Exclusion of discontinuations due to intolerability or reasons unrelated to treatment
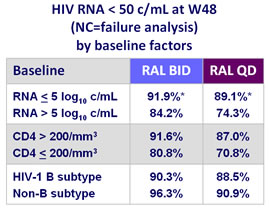
* 95% CI for the difference = - 8.3 ; 2.7
Mean CD4/mm3 increase at W48 (observed-failure analysis):
+ 196 (RAL BID) vs + 210 (RAL QD)
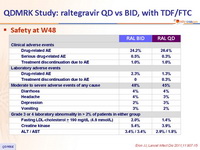
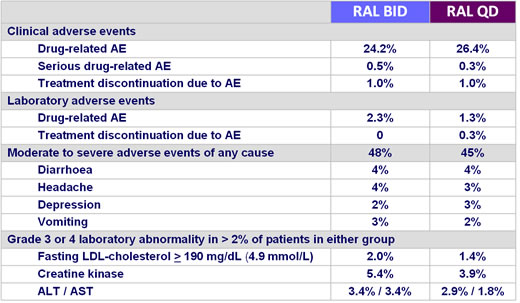
Safety at W48 :
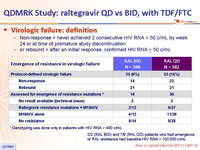
Virologic failure: definition
- Non-response = never achieved 2 consecutive HIV RNA < 50 c/mL by week 24 or at time of premature study discontinuation
- or rebound = after an initial response, confirmed HIV RNA ≥ 50 c/mL
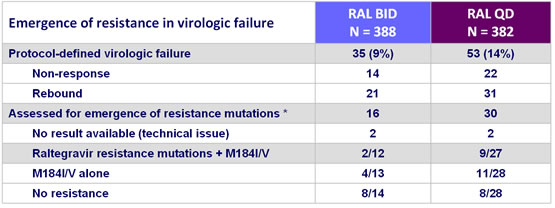
* Genotyping was done only in patients with HIV RNA > 400 c/mL
2/2 (RAL BID) and 7/9 (RAL QD) patients who had emergence of RAL resistance
had baseline HIV RNA > 100 000 c/mL
Pharmacokinetic Data :
- Trough raltegravir concentrations were more than six times higher with twice-daily dosing than they were with once-daily dosing
- Although an association between trough RAL concentrations and efficacy was evident in the once-daily group, no clear threshold could be identified